Is
that possible that one day the world could be completely reliant on
solar energy? To answer this question, we first need to examine how
solar panels work.
What are solar panels?
Solar panels (also known as PV modules) are the core component of the solar power system.
It directly influences the power efficiency of the solar power plant. A
single solar panel consists of many small PV cells. Each cell is made
of crystalline silicon, which can work as a semiconductor. When solar
panels are exposed to sunlight, they convert sunlight energy into
electricity.
How do solar panels work?
Solar
panels consist of smaller units called solar cells. The mainstream
solar cells are made from Silicon. It is a semiconductor that is the
second most abundant element on Earth. A solar cell is sandwiched
between conductive layers. Each silicon atom is connected to its
neighbors by four strong bonds which keep the electrons in place so that
no current can flow. What’s the key? A silicon solar cell has two
different layers of silicon, N-type silicon has extra electrons and
P-type silicon has extra spaces for electrons, called holes. Where the
two types of silicon meet, electrons can wander across the P/N junction,
leaving a positive charge on one side and creating a negative charge on
the other.
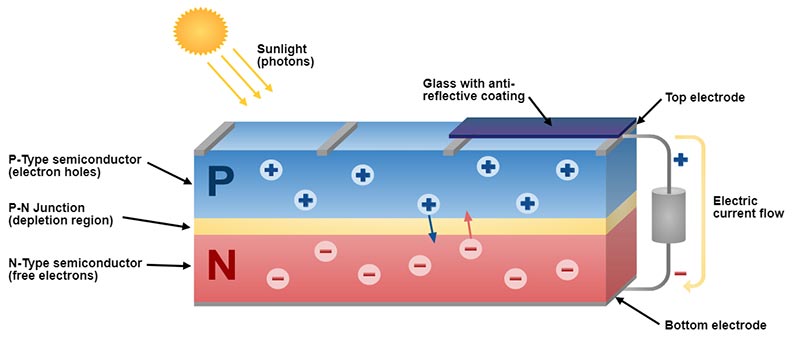
You
can think of light as the flow of tiny particles called photons,
shooting out from the sun. When one of these photons strikes the silicon
cells with enough energy, it can knock an electron from its bond,
leaving a hole. The negatively charged electrons and location of the
positively charged holes are now free to move around. But because of the
electric field at the P/N junction, they’ll only go one way. The
electron is drawn to the N-side, while the hole is drawn to the P-side.
The mobile electrons are collected by thin metal fingers at the top of
the cell. From there, they flow through an external circuit, doing
electrical work, like powering a light bulb, before returning through
the conductive aluminum sheet on the back. Each silicon cell only puts
out half a volt, but you can string them together in modules to give
more power.
You can read more about the specifics of the how solar panels work in this blog post if you want to learn more.
Types of solar panel
Currently, there are three types of solar panels in common according to the PV cells: monocrystalline solar panels, polycrystalline PV modules, and thin film solar panels.
A
monocrystalline photovoltaic panel is made of high-purity
monocrystalline silicon rods, which are widely used in the photovoltaic
industry and have a high photoelectric conversion rate; the four corners
of monocrystalline PV cells are rounded, and their color is nearly
black; besides, the crafts of monocrystalline cells are more complex and
thus the cost is higher.
Polycrystalline photovoltaic
modules component of polycrystalline solar cells arrayed in various
series and parallel configurations. The four corners of the PV cells are
square. Moreover, it is colored sky blue, and the cost of the poly
solar panel is lower compared to mono panels.
The
thin-film solar panel is made of thin films of semiconductors deposited
on glass, plastic, or metal. The films are incredibly thin, often 20
times thinner than c-Si wafers. This makes thin-film solar panels
flexible and lightweight. It has high power efficiency under certain
situations, like under shading or high temperature.
Conclusion Solar
power is getting better, cheaper, and competing with the electricity
from the grid. And innovations, like Topcon cells and HJT cells, may
bring solar panels a brighter future.